ECOM6013 E-Commerce Technologies
Topic 2 Internet and E-Commerce Infrasture
Internet
- Interconnected network of thousands of networks and hundreds of millions of computers
- Links businesses, educational institutions, government agencies, and individuals
World Wide Web (WWW)
- One of the internet’s most popular services
- Provides access to billions, possibly trillions, of Web pages
Evolution of Internet
- Innovation phase (1961 - 1974)
- Institutionalization phase (1975 - 1995)
- Commercialization Phase (1995 - present)
Packet Switching
- Slices digital messages into packets
- Sends packets along different communication paths as they become available
- Reassembles packets once they arrive at destination
It uses routers (special purpose computers that interconnect the computer networks that make up the internet and route packets)
Less expensive, wasteful than circuit-switching
TCP/IP
Four TCP/IP Layers
- Application layer (HTTPS - Web, Telnet - Terminal, FTP - Files, SMTP - E-mail)
- Transport layer (TCP)
- Internet layer (IP)
- Network interface layer (Ethernet)
IPv4
- 32-bit number (handle up to 4 billion addresses)
- Four sets of numbers (201.61.186.227)
IPv6
- 128-bit number (handle up to 1 quadrillion addresses)
Domain Names, DNS, and URLs
- Domain Name: IP address expressed in natural language
- Domain Name System (DNS): Allows numeric IP addresses to be expressed in natural language
- Uniform resource locator (URL): Address used by Web browser to identify location of content on the Web
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
How computer gets its IP Address
Client/Server Computing
Powerful personal computers (clients) connectd in network with one or more servers
- Storing files
- Software applications
- Access to printers, and so on
The Mobile Platform
- Tablets
- Smartphones (disruptive technology): New processors & New operating systems
Cloud Computing
Firms and individuals obtain computing power and software over Internet (public, private and hybrid clouds)
Three Types of Services
- Infrasture as a service (IaaS)
- Software as a service (SaaS)
- Platform as a service (PaaS)
Reduces Cost of
- Building and operating Websites
- Infrasture, IT support
- Hardware, software
Drawbacks
- Security risks
- Shifts responsibility for storage and control to providers
Internet Infrasture
Internet growth has boomed without disruption because of
- Client/server computing mode
- Hourglass, layered architecture
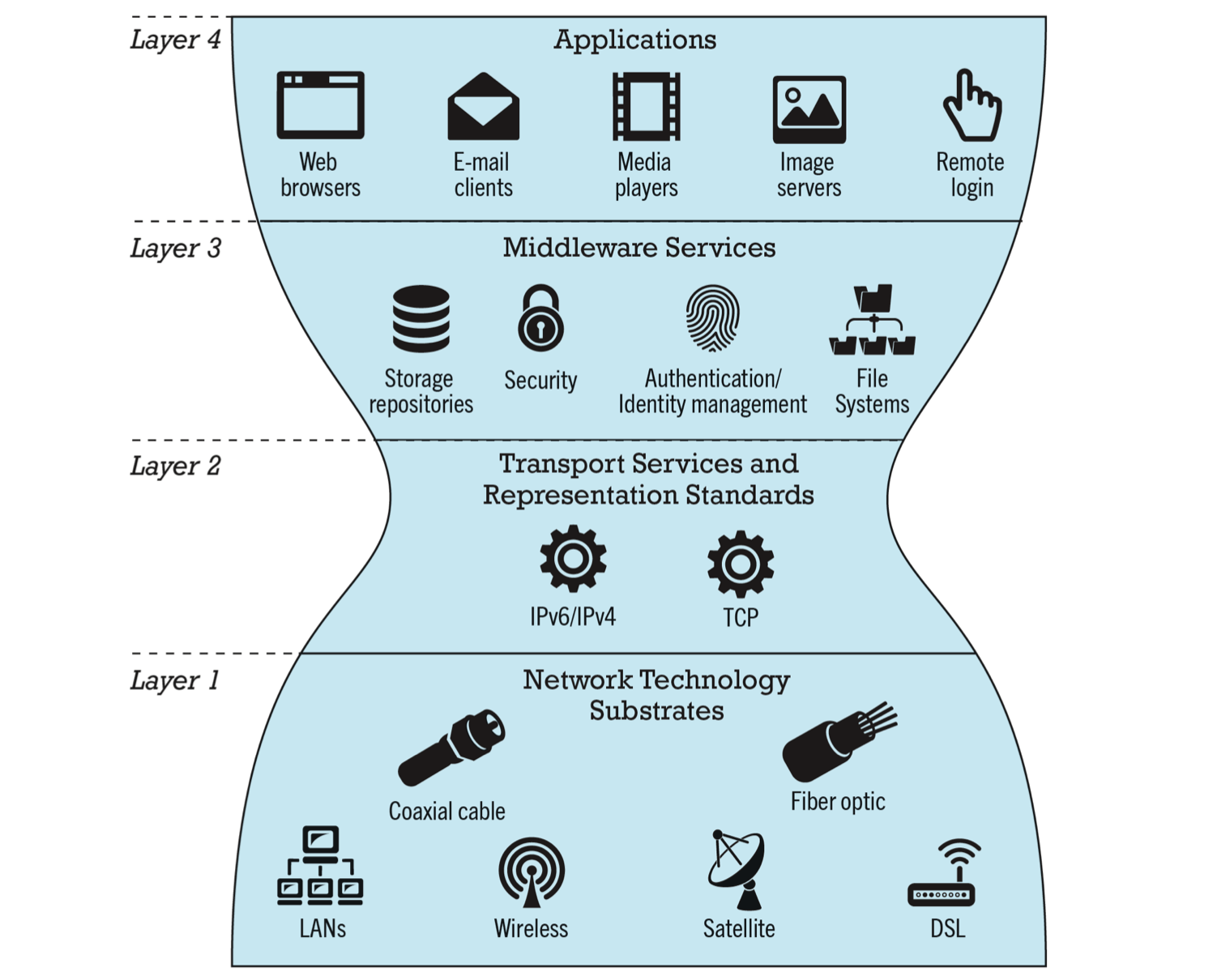
- Applications
- Middleware Services
- Transport Services and Representation Standards
- Network Technology Substrate
Internet Network Architecture
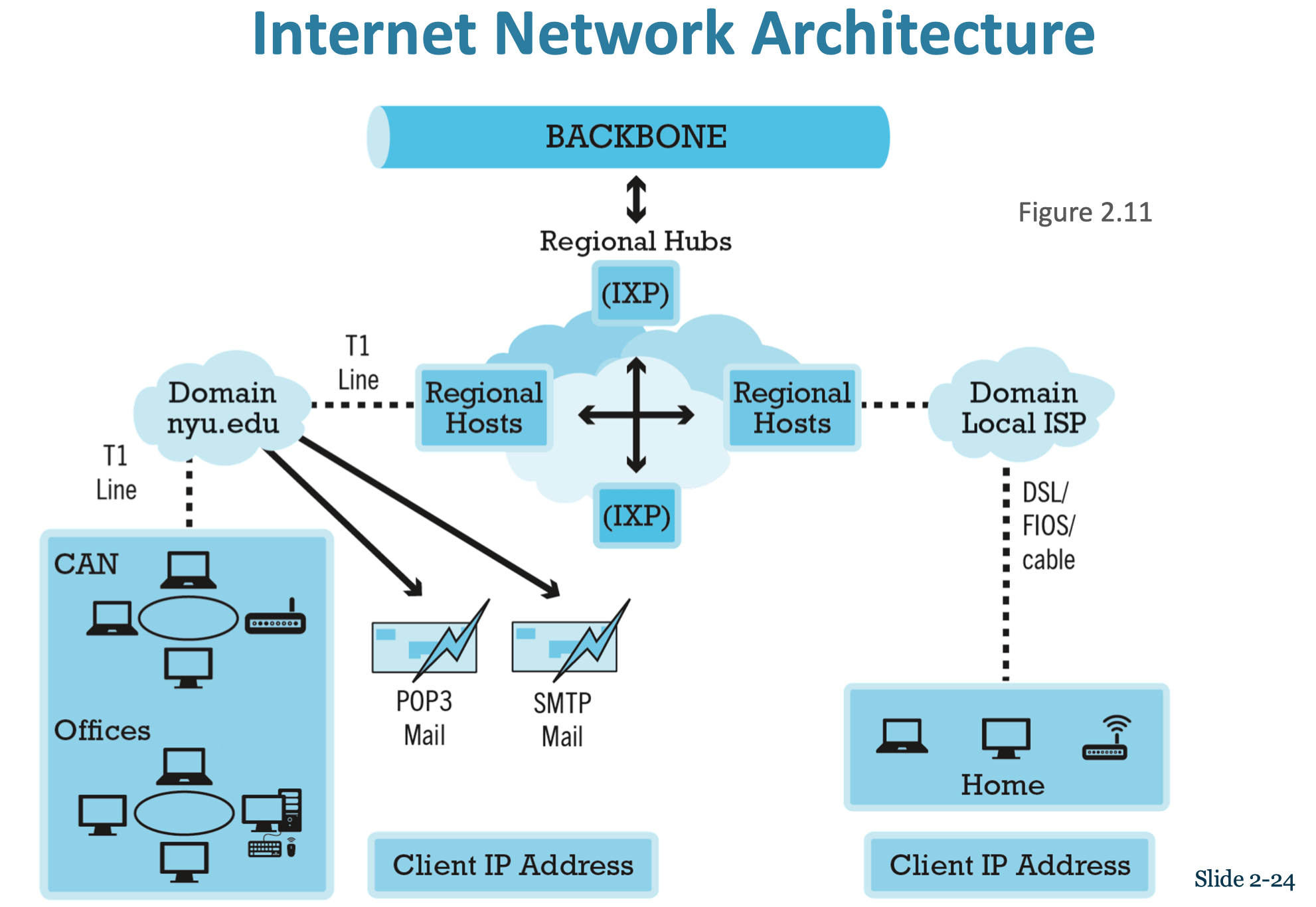
The Internet Backbone
Comprised of fiber-optic cable
- Faster speeds and greater bandwidth
- Thinner, lighter cables
- Less interference
- Better data security
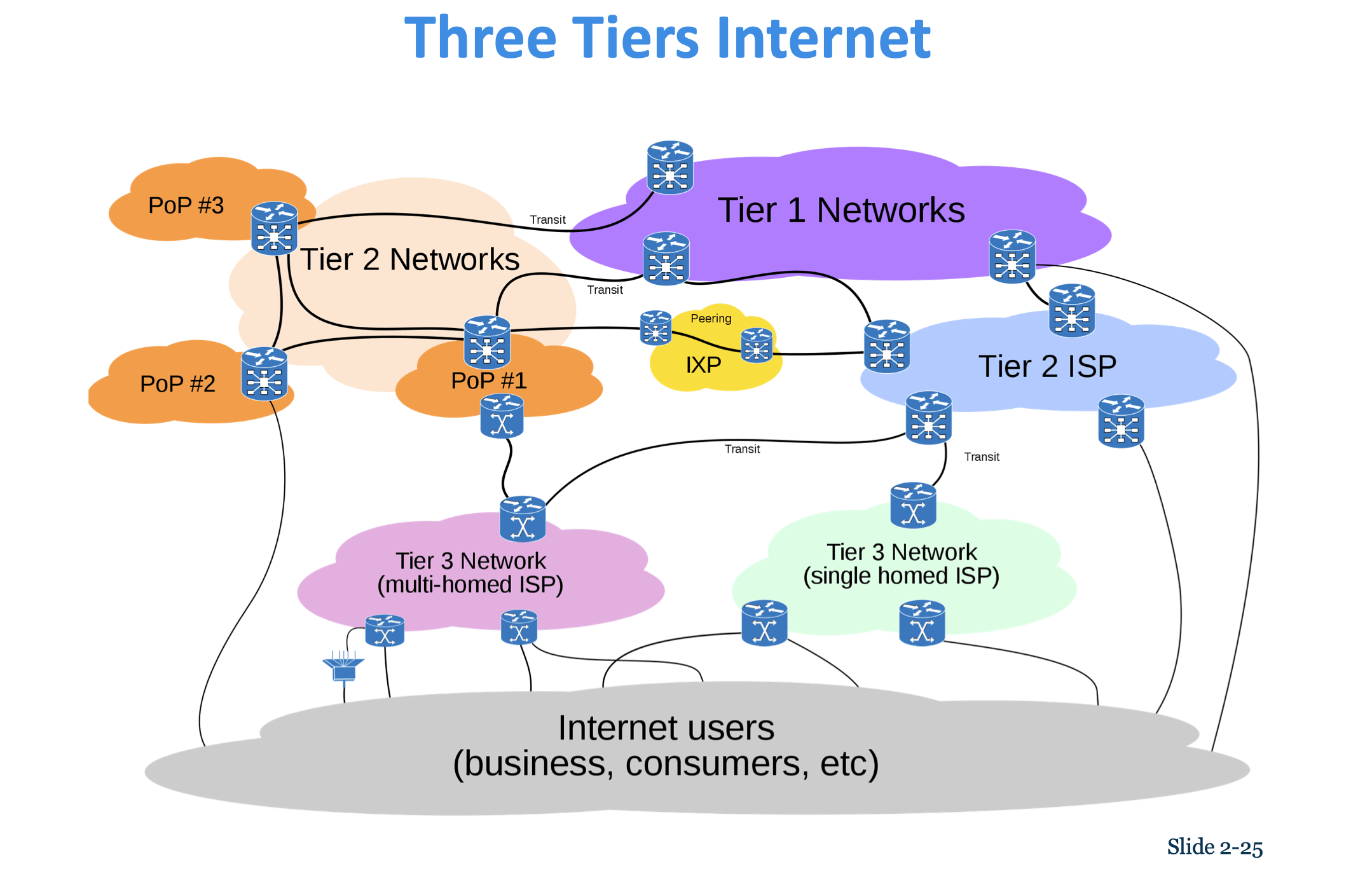
Tier 1 Internet Service Providers (Tier 1 ISPs) or transit ISPs
Numberous private networks physically connected to each other
Underseas fiber optics, satellite links
Internet Exchange Points (IXPs)
Originally called Network access Points (NAPs) or Metropolitan Area Exchanges (MAEs)
- Regional hubs where Tier 1 ISPs physically connect with one another and with regional Tier 2 ISPs
- Tier 2 ISPs provide Tier 3 ISPs with Internet access
Tier 3 Internet Services Providers
Services
- Narrowband
- Broadband
- Digital subscriber line (DSL)
- Cable Internet
- Satellite Internet
Campus/Corporate Area Networks
- Local area networks operating within single organization
- Lease Internet access directly from regional and national carriers
Mobile Internet Access
Telephone-based
- 3G/4G technologies now
- 5G - higher bandwidth (10 Gbps), lower latency
Computer network-based (wireless local area network-based)
- Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11 standards)
- High speed, fixed broadband wireless LAN (WLAN)
- Wireless access point (Hot Spots)
- Limited range but inexpensive
- Zigbee, Bluetooth, BLE
- Low-power WAN - LoRaWan
Intranets
- TCP/IP network located within a single organization for communications and processing
- Used by private and government organizations for iternal networks
- All Internet application can be used in private intranets
The Internet of Things (IOT)
- Objects connected via sensors/RFID to Internet
- Interoperability issues and standards
- Security and privacy concerns
“Smart things”
Limitations of the Current Internet
Bandwidth
- Slow peak-hour service
Quality of Service
- Lantency
Network Architecture
- Identical requests are processed individually
Wired Internet
- Copper and expensive fiber-optic cables
Who Governs the Internet?
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- Internet Research Task Force (IRTF)
- Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG)
- Internet Architecture Board (IAB)
- Internet Society (ISOC)
- Internet Governance Forum (IGF)
- World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
- Internet Network Operators Groups (NOGs)
The Web
- Web invented (1989 - 1991)
- Mosaic web browser w/GUI (1993)
- Netscape Navigator, first commerical web browser (1994)
- Microsoft Internet Explorer (1995)
Hypertext
- Text formatted with embedded links
- Use Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and URLs to locate resources on the web
Markup Languages
- HTML - Hypertext Markup Language
- XML - eXtensible Markup Language (Tags used are defined by user)
Web Servers and Clients
- Web server (web servers or physical server)
- Web server softwares (FTP, search engine, data capture, security services)
- Web client (capable of making HTTP requests and displaying HTML pages)
Features of the Internet and Web
- Communication Tools
- Messaging application
- Online message boards
- Internet telephony (VOIP)
- Video conference, video chat, teleprence…
- Search Engines (Google, Bing, Yahoo, baidu,…)
- Identify web pages that mach queries based
- Keyword indexes
- Page ranking
- Identify web pages that mach queries based
- Downloadable and Streaming Media
- Downloads
- Streaming technologies
- Podcasting
- Online video viewing (Explosion)
- Web 2.0 Features and Services
- Online Social Networks
- Blogs
- Wikis
- VR and AR
- Virtual reality - VR
- Augmented reality - AR (Pokemon Go)
- Intelligent Digital Assistants
- Used by search engine
- Natural language
- Conversational interfaces, verbal commands
- Situation awareness
- Intelligent Assistants
- Apple Siri
- Amazon Alexa
- Google Assistant
- Xiaomi Xiaoai
- Used by search engine
- Mobile Apps
- Wide range of use
- Platforms - IOS, Android…
- Marketplaces - App Store, Google Play…
