ECOM6013 E-Commerce Technologies
Topic 5 Mobile Commerce
Basic Principle of Mobile Technology
- FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access)
- TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access)
- CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access)
Fundamental Mobility: Cellphones
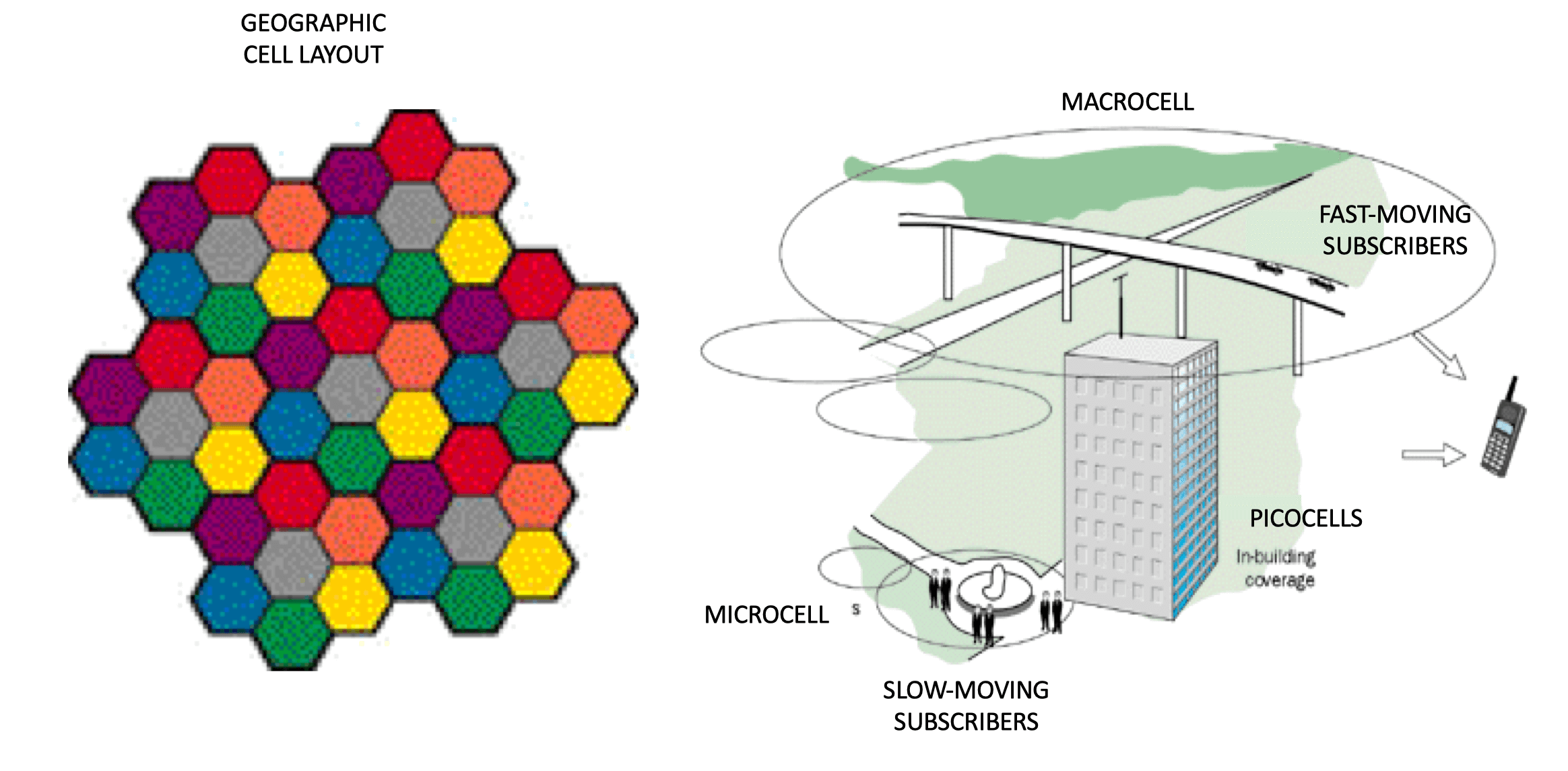
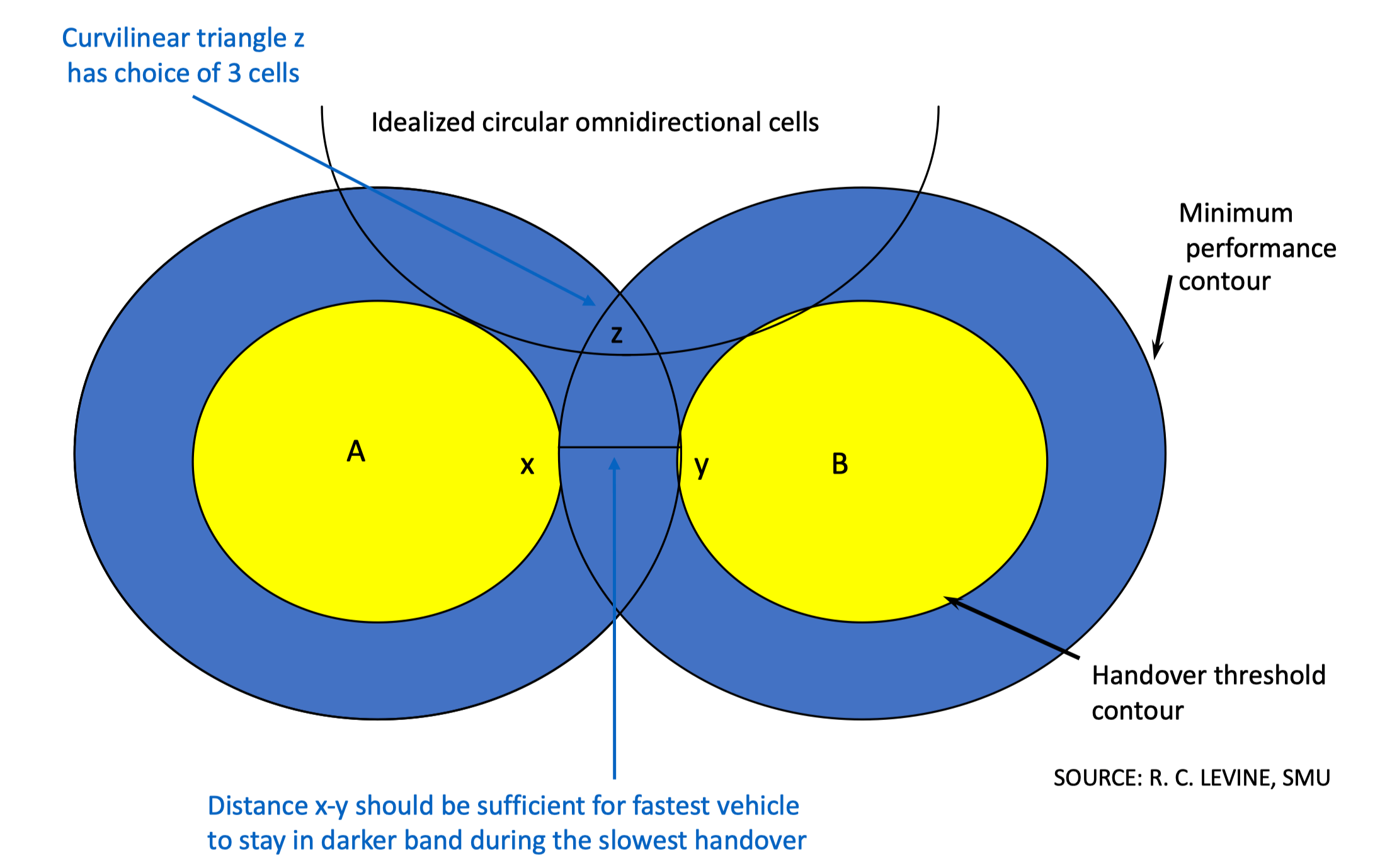
Cell Handover
4G vs. 5G
- 4G
- 10 ms
- 100 Thousand Connections / km^2
- 1 Gbps
- 5G
- < 1ms
- 1 Million Connections / km^2
- 20 Gbps
E-Commerce vs. M-Commerce
- E-Commerce
- Device: PC
- Network: Internet (HTTP)
- M-Commerce
- Device: Mobile devices
- Network
- Mobile carrier network
- WiFi
- Local frequency (RFID/NFC)
Definition of M-Commerce
- Buying and Selling via mobile devices
- Paying via mobile devices
- Use of any technologies to support the above
Mobile Devices
- Devices
- Mobile phone/smart phone
- Tablet computer
- Wearable technology
- …
- Usages
- Transact
- Communicate
- Entertain
Roles in M-Commerce
- Users
- End users/system users
- Suppliers
- Network operators (offer transport facility and network infrastructure)
- Service providers (develop new devices)
- Content providers (aggregate contents)
- Commerce mediators (provide solutions and services)
- Finance organizations (provide framework and infrasture for payment)
- Mobile device (interacting with all roles)
M-Commerce Services and Applications
- Sevices
- Mobile ticketing
- Mobile money transfer
- Conetent purchase and delivery
- Information services
- Mobile banking
- Mobile browsing
- Mobile purchase
- Mobile marketing and advertising
- …
- Applications
- Entertainment
- Music
- Games
- graphics
- Video
- …
- Communications
- Short messaging
- Multi-media messaging
- Unified messaging
- Social
- Video conferencing
- …
- Transactions
- Banking
- Broking
- Shopping
- Auctions
- Betting
- Booking & reservations
- Mobile wallet
- Mobile purse
- …
- Information
- News
- City guides
- Directory services
- Maps
- Traffic and weather
- Corporate information
- Market data
- …
- Entertainment
PTDs (Personal Trusted Devices)
- Location and orientation
- Multiple types of networking (NFC/Bluetooth)
- Accelerometers
- Camera
- …
QR Code (Quick Response Code)
- Originally designed as a two-dimensional barcode (not for mobile)
- Standardized (ISO/IEC 18004:2006)
- Oatented (but free license)
Other Enabling Technologies
- GPS
- Widely available on most devices
- Geo-loctaion and geo-fencing
- Doesn’t work inside buildings
- High battery consumption
- NFC/RFID
- Great accuracy
- Low cost
- Not support on all devices
- 20cm range
- High battery consumption
Obstacles
- Mobile device power
- GPS/network calls cost hign power
- Privacy
- Continuous tracking
- Network
- Bandwidth
- Congestion
- Processing speed
Related Posts
Comments
