前言 #
目前工作中负责一个针对 Hyperledger Fabric 的区块链即服务 (Blockchain as a Service, BaaS) 平台的链码管理部分,对这 BaaS 平台的架构与实现很感兴趣,作为一个能为开发者提供一站式应用创建、管理和维护区块链的平台,其架构是怎么样的呢?
本文是对 BaaS 平台架构的总结和梳理。
BaaS 简介 #
区块链是一个复杂的分布式系统,尤其是像 Hyperledger Fabric 这样的企业联盟链平台,其部署和运维都非常复杂,作为应用开发者需要处理许多环境问题(如证书、docker 环境等),带来了许多挑战。
因此,BaaS 平台应运而生,它是一种帮助用户创建、管理和维护企业级区块链的应用平台,用户能够通过友好的 Web 界面对区块链进行操作。通过 BaaS 平台,用户可以很灵活地搭建区块链网络、管理区块链业务和各个模块的功能、进行智能合约的研发和部署以及实时监控和运维。
通过 BaaS 平台,开发者可以快速进行区块链业务的研发,综合成本大大降低,且有助于系统稳定性、安全性和易用性等的提升。
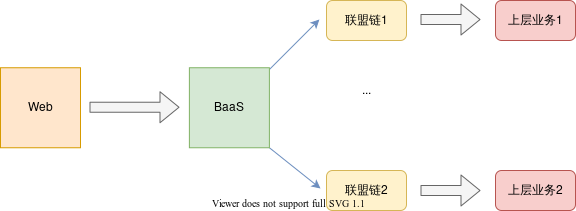
平台架构 #
BaaS 平台作为一个一站式应用服务,自下而上主要分为以下几层:
- 资源层
- 监控运维层
- 区块链底层
- 区块链服务层
- 应用层
而根据每个系统的业务差异,各个层的架构与功能模块会有所差异,下面将会对几大主流平台层次结构做一些描述。
Hyperledger Cello #
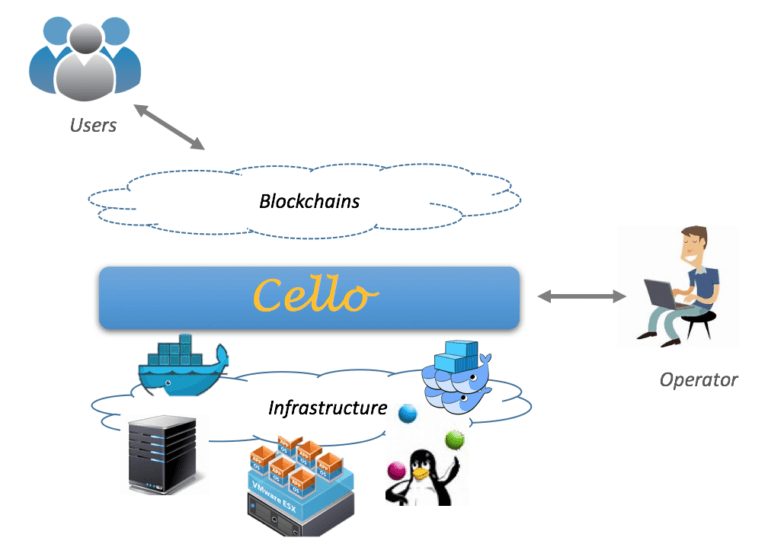
Hyperledger Cello 作为 IBM Hyperledger 的顶级项目之一,是一个开源区块链管理平台,支持部署、运行时管理和数据分析等功能。
Cello 目前支持 Hyperledger Fabric 区块链,可以有效管理 Fabric 链的生命周期,主要包含以下模块:
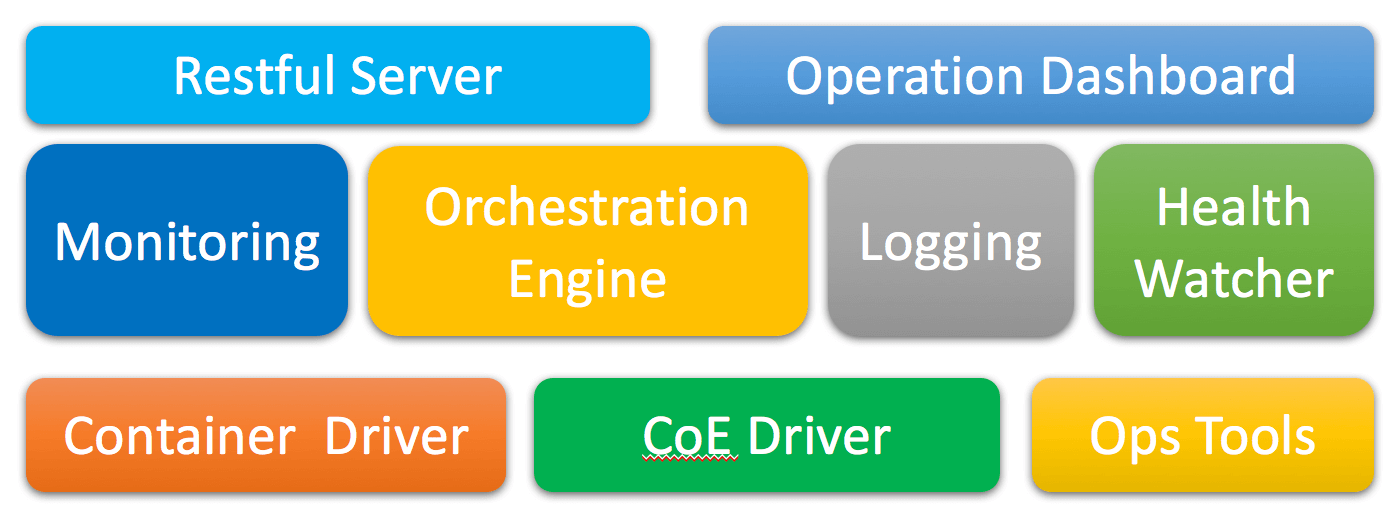
除了高效地创建部署网络外,Cello 提供了一些对于区块链的管理功能:
- 区块链生命周期管理
- 底层支持多种架构,如 Docker、Swarm、Kubernetes 等
- 支持多种底层区块链平台并可以自定义配置
- 支持运行时监控与运维
- 可插拔的框架设计,可以通过插件的形式拓展第三方功能,如资源调度、驱动代理等
趣链 BaaS #
根据官网介绍,BlocFace 是由趣链科技为企业及开发者全新推出的区块链服务平台,为用户提供一键部署联盟链、可视化监控运维和智能合约研发等一站式研发服务,其平台架构如下:

总结 #
以上就是对区块链服务平台 (BaaS) 的简介及架构分析,因为目前的 Leader 是 Hyperledger Cello 的项目发起人和核心开发者,鼓励我积极参与 Cello 的开源建设,要加油啦!