ECOM6013 E-Commerce Technologies #
Topic 6 E-Commerce Security #
Good E-Commerce Security
- Highest degree of security
- New technologies
- Organizational policies and procedures
- Industry standards and government law
- Other factors
- Cost of security vs. potential loss
- Security often breaks at weakest link
The Tense Between Security and Other Values
- Security vs. Easy of use
- More Secure -> More difficult to use + slower
- Security vs. Desire of individuals to act anonmously
Basic E-Commerce Security Issues and Landscape
- E-Commerce security requirements
- Authentication (verify the real identity)
- Authorization (determine the entity’s access)
- Auditing
- Availability
- Nonrepudiation (assurance that trading partners can’t falsely deny their purchase or transaction)
- Risk (a vulnerability will be known and used)
- Social engineering (non-technical attack, trick users to do some certain actions)
- Spam
E-Commerce of Today
- Threats
- Money thefts
- Identity thefts
- Malware
- Solutions
- Authentication
- Intrusion checking
- Firewalls
- Education
Security Threats in the E-Commerce Environment
- Three key points of vulnerability
- Client
- Server
- Communication pipeline (network channels)
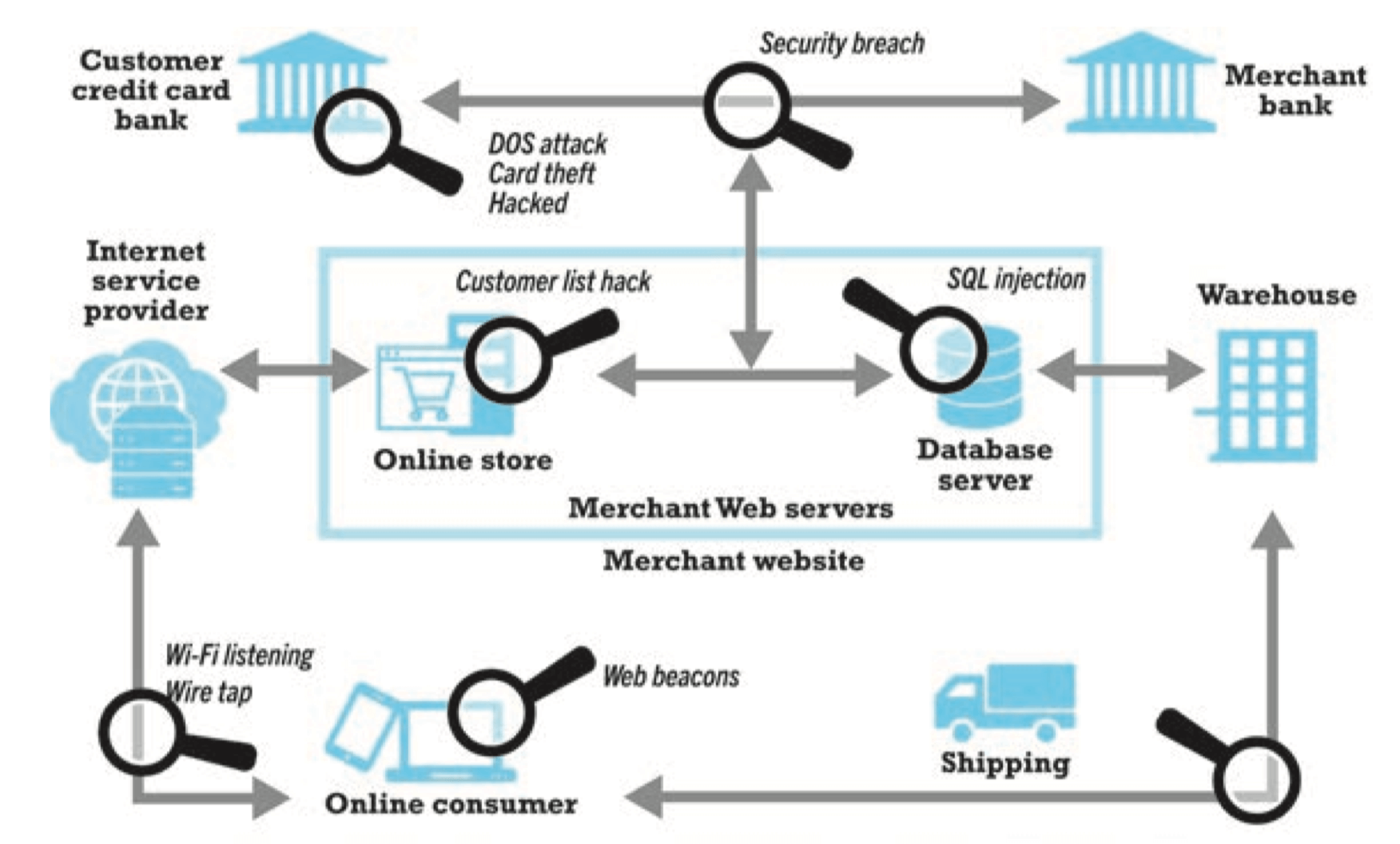
Most Common Security Threats
- Malicious code
- Viruses
- Worms
- Ransomeware
- Trojan horses
- Backdoors
- Bots, botnets
- Unwanted programs
- Browser parasites
- Adware
- Spyware
- Phishing
- Deceptive online attack to obtain confidential information
- Social engineering, e-mail scams, spoofing legitimate websites
- Used for identity fraud and theft
- Hacking and cybervandalism
- Hackers vs. Crackers
- Cybervandalism (intentionally disrupting, defacing, destroying websites)
- Hacktivism
- Data breach
- Credit card fraud/theft
- Spoofing
- Pharming
- Spam / junk websites
- Denial of sevices (DoS) attack (useless traffic to overwhelm network)
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack (multiple computers to attack target network)
- Sniffing (eavesdropping program that monitors information traveling over a network)
- Insider jobs
- Single financial threats
- Poorly designed security policy and server / client software
- Social network issues
- Mobile platform issues
- Cloud security issues
- IoT security issues
The Information Assurance Model and Defense Objectives
- CIA security triad
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
Three Dimensions in Internet Security
- Integrity
- Nonrepudiation
- Authenticity
- Confidentiality
- Privacy
- Availability
Technology Solutions
- Protecting internet communications
- Cryptography
- Securing channels of communication
- SSL, TLS
- Establishes a secure, negotiated client-server session in which URL of requested document, along with contents, is encrypted
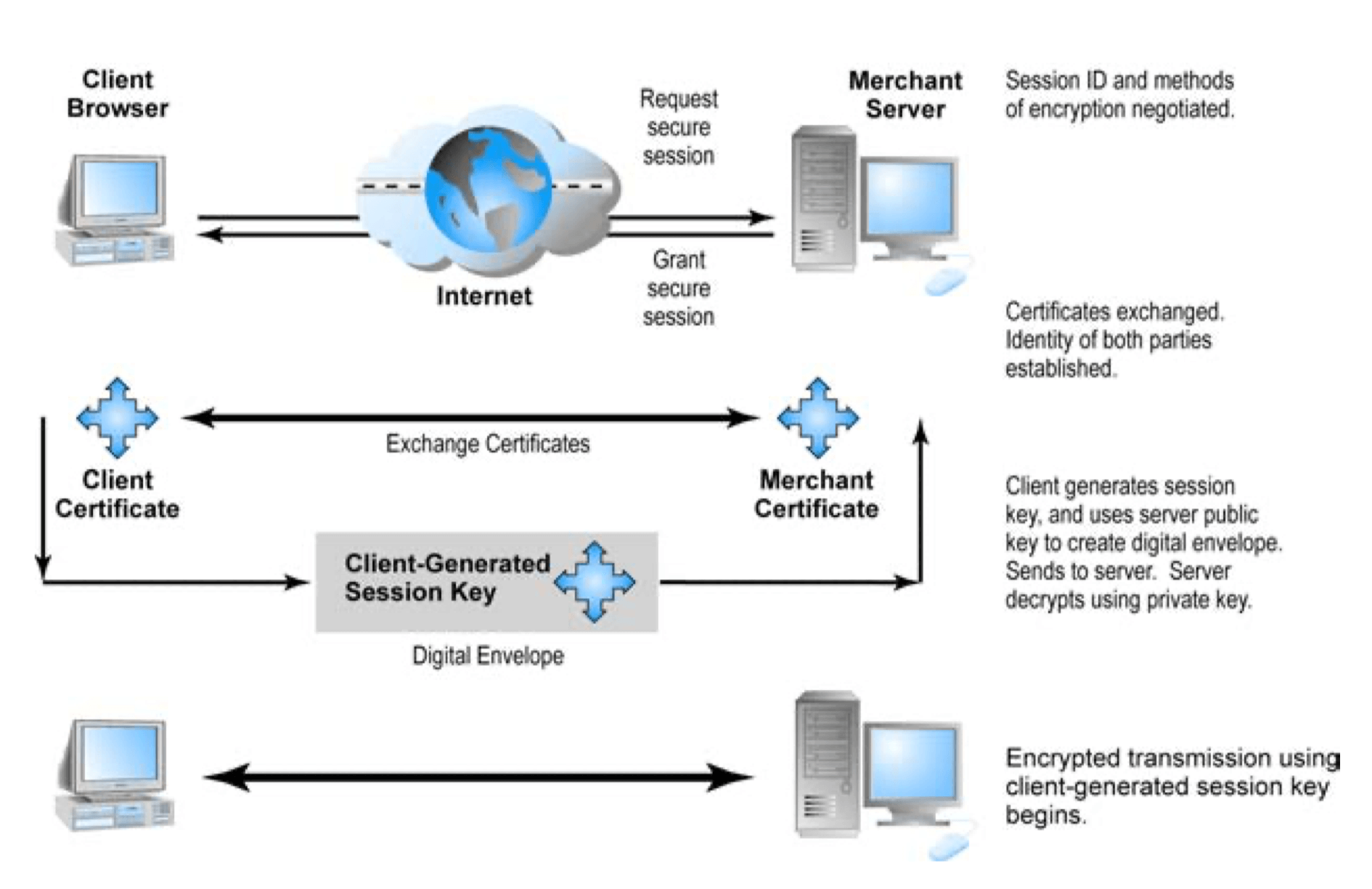
- S-HTTP
- Provides a secure message-oriented communications protocol designed for use in conjunction with HTTP
- VPNs
- Allows remote users to securely access internal network via the Internet, using Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
- Wi-Fi
- SSL, TLS
- Protecting networks
- Firewalls
- Proxy servers
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
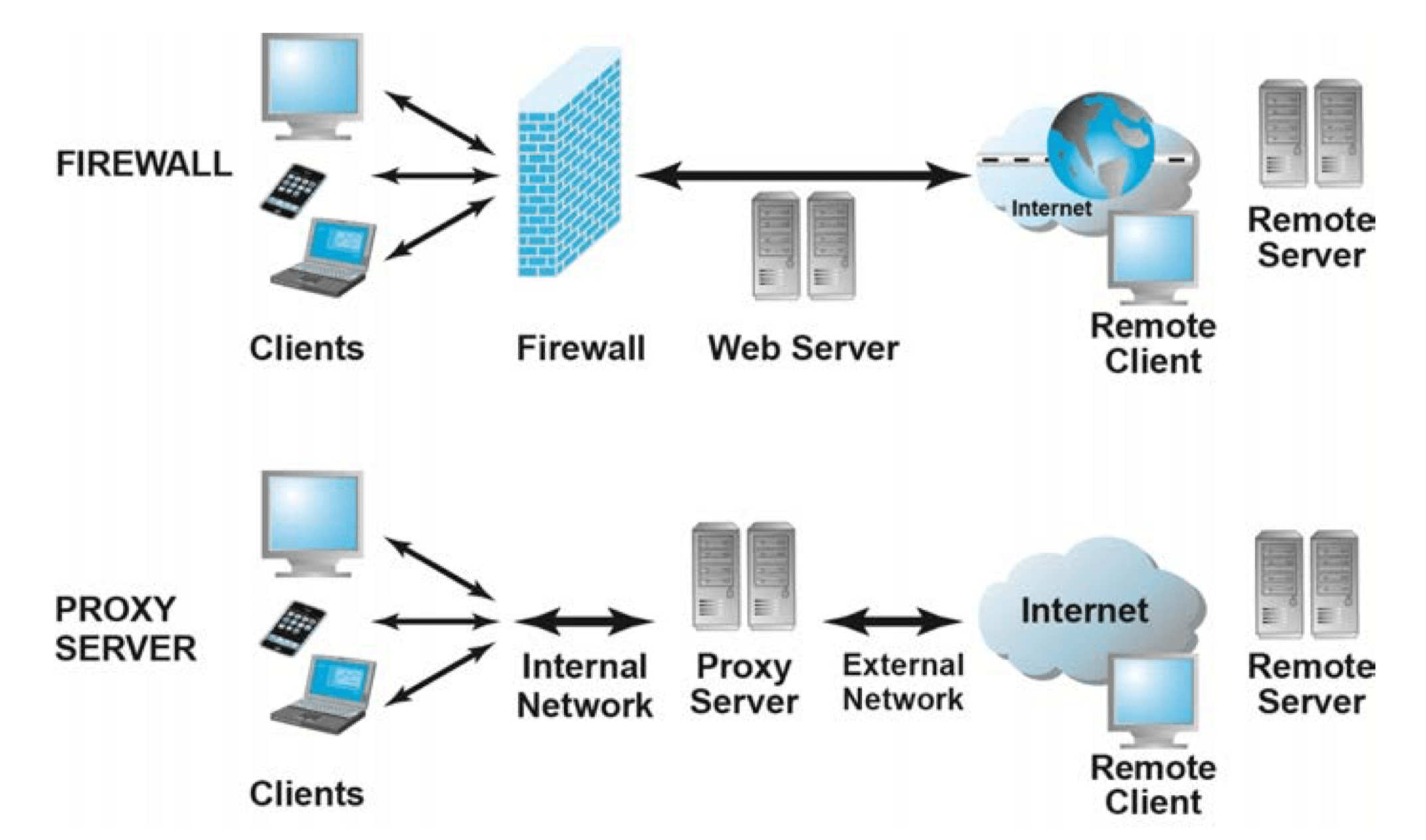
- Protecting servers and clients
- OS security
- Upgrades
- Patches
- Anti-virus software
- Easiest and least expensive way to prevent threats to system integrity
- Requires daily updates
- OS security
Managing Risks
- Technology
- Effective management policies
- Public laws and active enforcement
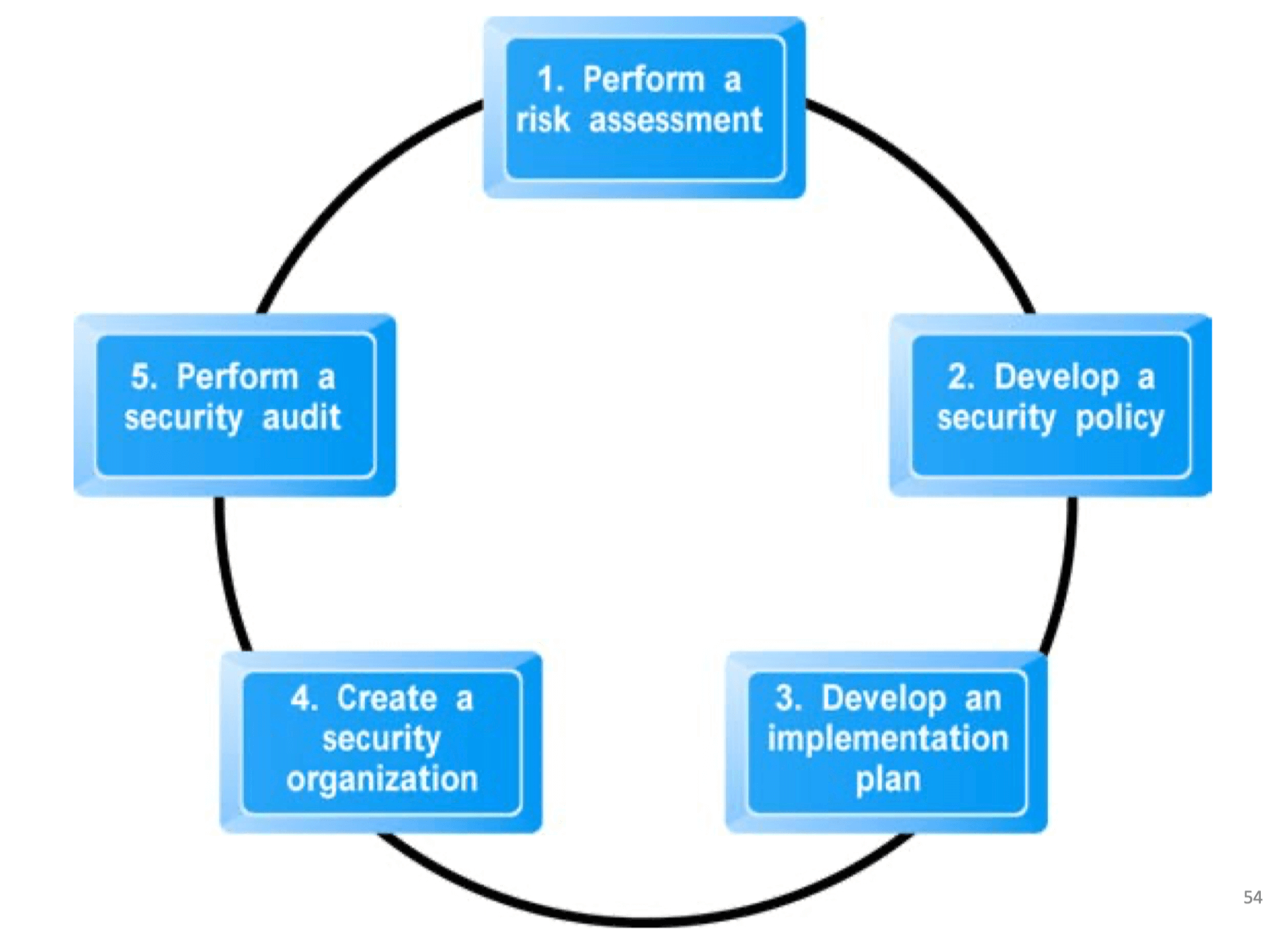
A Security Plan: Management Policies
- Risk assessment
- Security policy
- Implementation plan
- Security organization
- Access controls
- Authentication procedures, including biometrics
- Authorization policies, authorization management systems
- Security audit
Basic Concepts of User Authentication
- Something you know
- Password
- PIN
- OTP
- …
- Something you have
- Physical key
- Token
- Magnetic card
- Smartcard
- …
- Something you are
- Fingerprint
- Voice
- …
Best use 2 Factors Authentication (2FA)
Encryption
- Transfer data into cipher text readable only by sender and receiver
- Secures stored information and information transmission
- Provide 4/6 key dimensions of E-Commerce security
- authentication
- Confidentiality
- Message Integrity
- Nonrepudiation
Symmetric Key Cryptography
- Sender and receiver use same digital key to encrypt and decrypt message
- Requires different set of keys for each transaction
- Strength of encryption
- Length of binary key used to encrypt data
- Standards
- Data Encryption Standard (DES, 1977)
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES, 2000)
- Other standards use keys with up to 2,048 bits
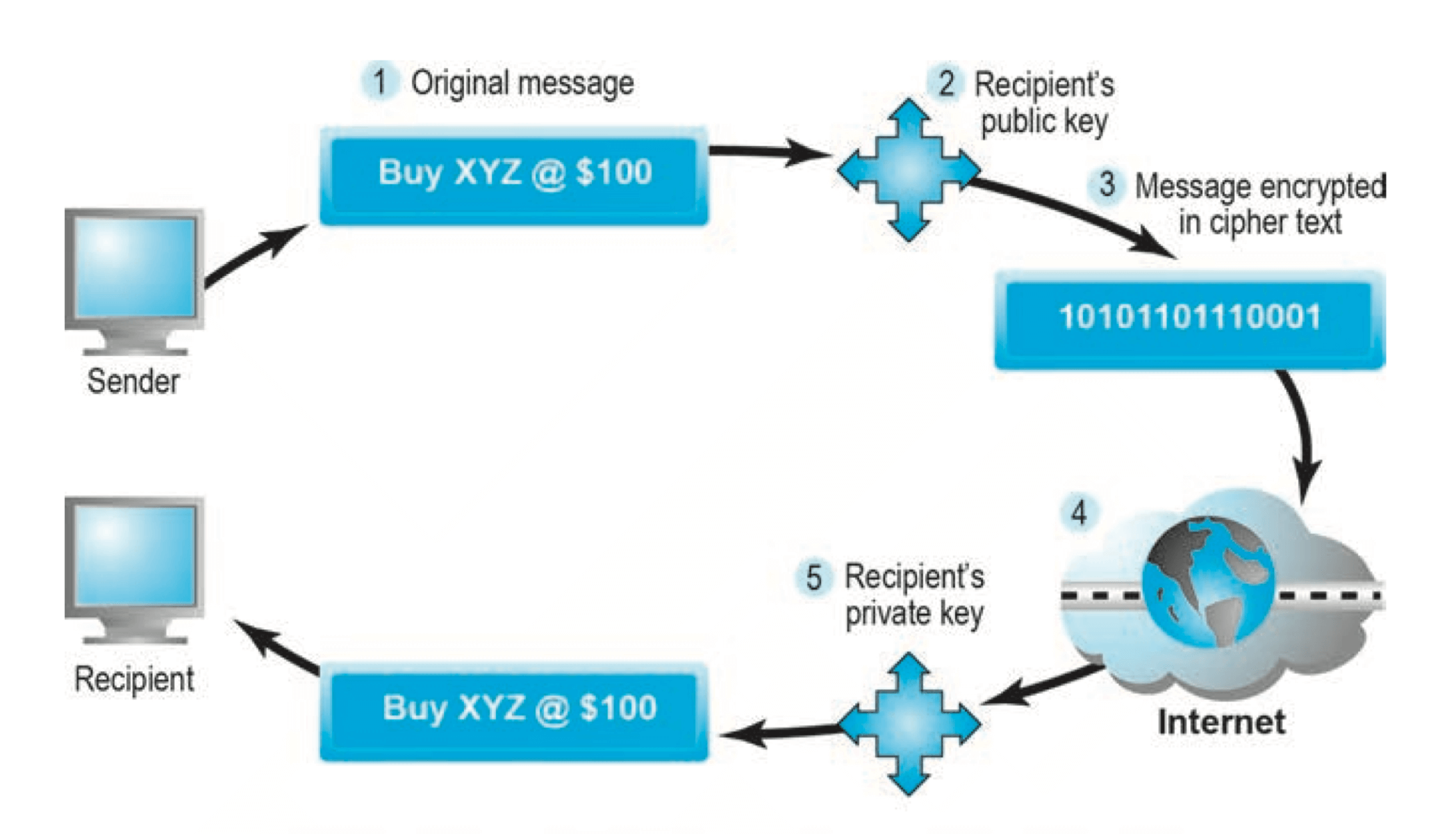
Public Key Cryptography
- Uses two mathematically related digital keys
- Public key (widely disseminated)
- Private key (kept secret by owner)
- Both keys used to encrypt and decrypt message
- Once key used to encrypt message, same key cannot be used to decrypt message
- Sender uses recipient’s public key to encrypt message
- Recipient uses his/her private key to decrypt it
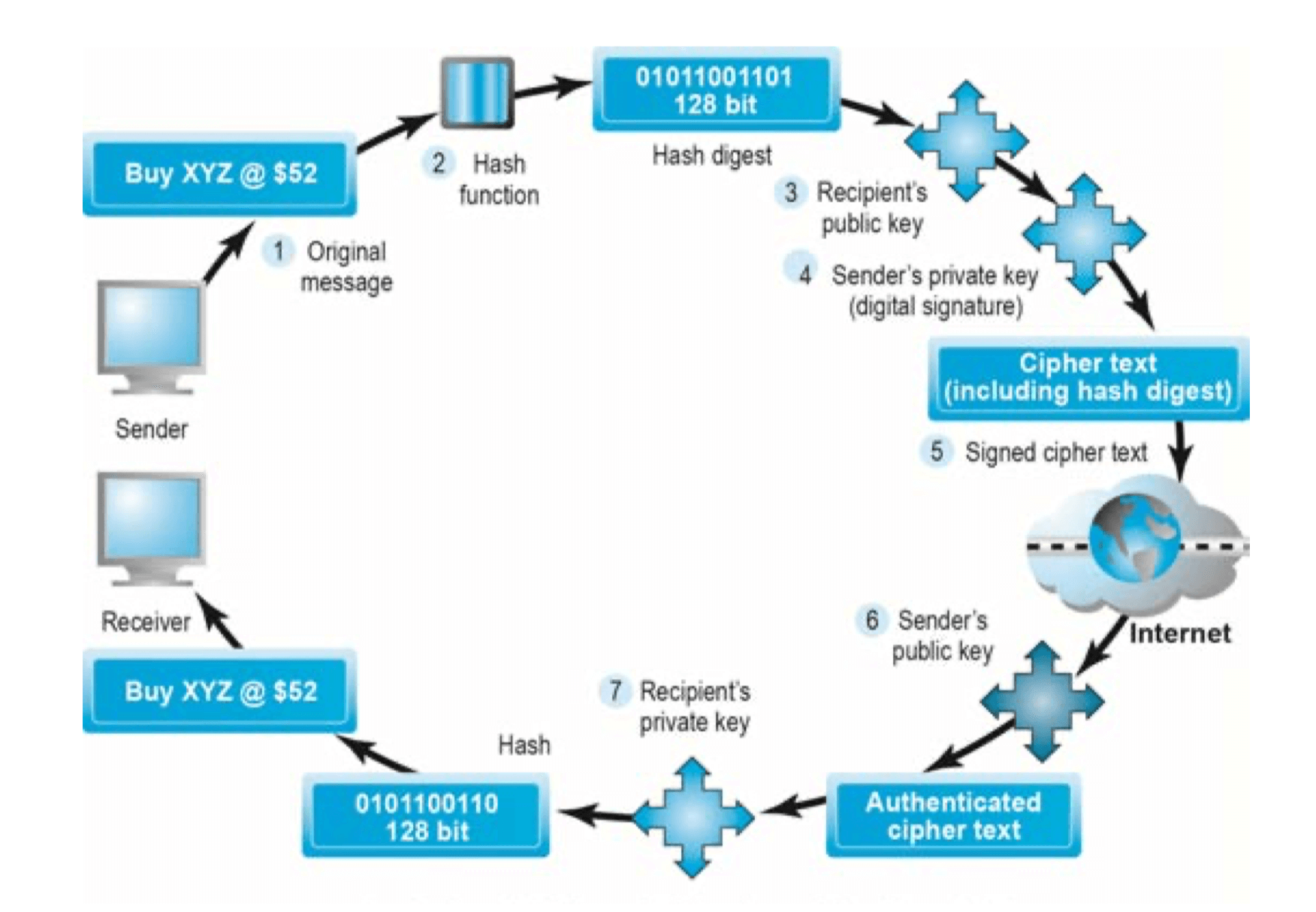
Public Key Encryption Using Digital Signatures and Hash Digests
- Hash function
- Mathematical algorithm (e.g. MD5 and SHA-1) that produces fixed-length number called message or hash digest
- Sender applies hash function to the message and then encrypts the message AND the hash digest with recipient’s public key
- Sender then encrypts the whole package with sender’s private key, creating digital signature for authenticity, nonrepudiation
- Recipient first uses sender’s public key to authenticate the message and then the recipient’s private key to decrypt the hash digest and the message
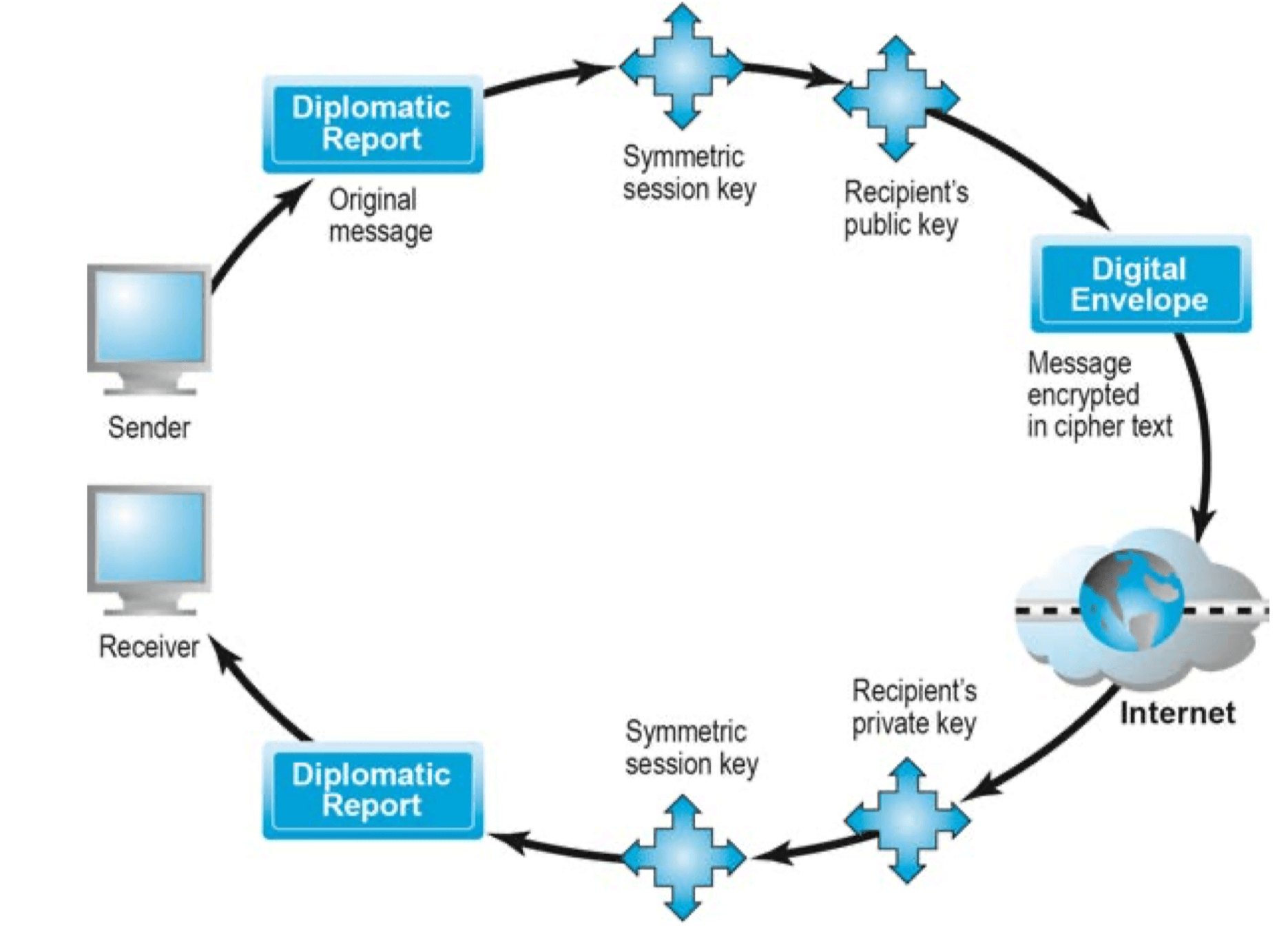
Digital Envelop
- Addresses weaknesses of
- Public key encryption (computationally slow)
- Symmetric key encryption (insecure transmission lines)
- Uses symmetric key encryption to encrypt document
- Uses public key encryption to encrypt and send symmetric key
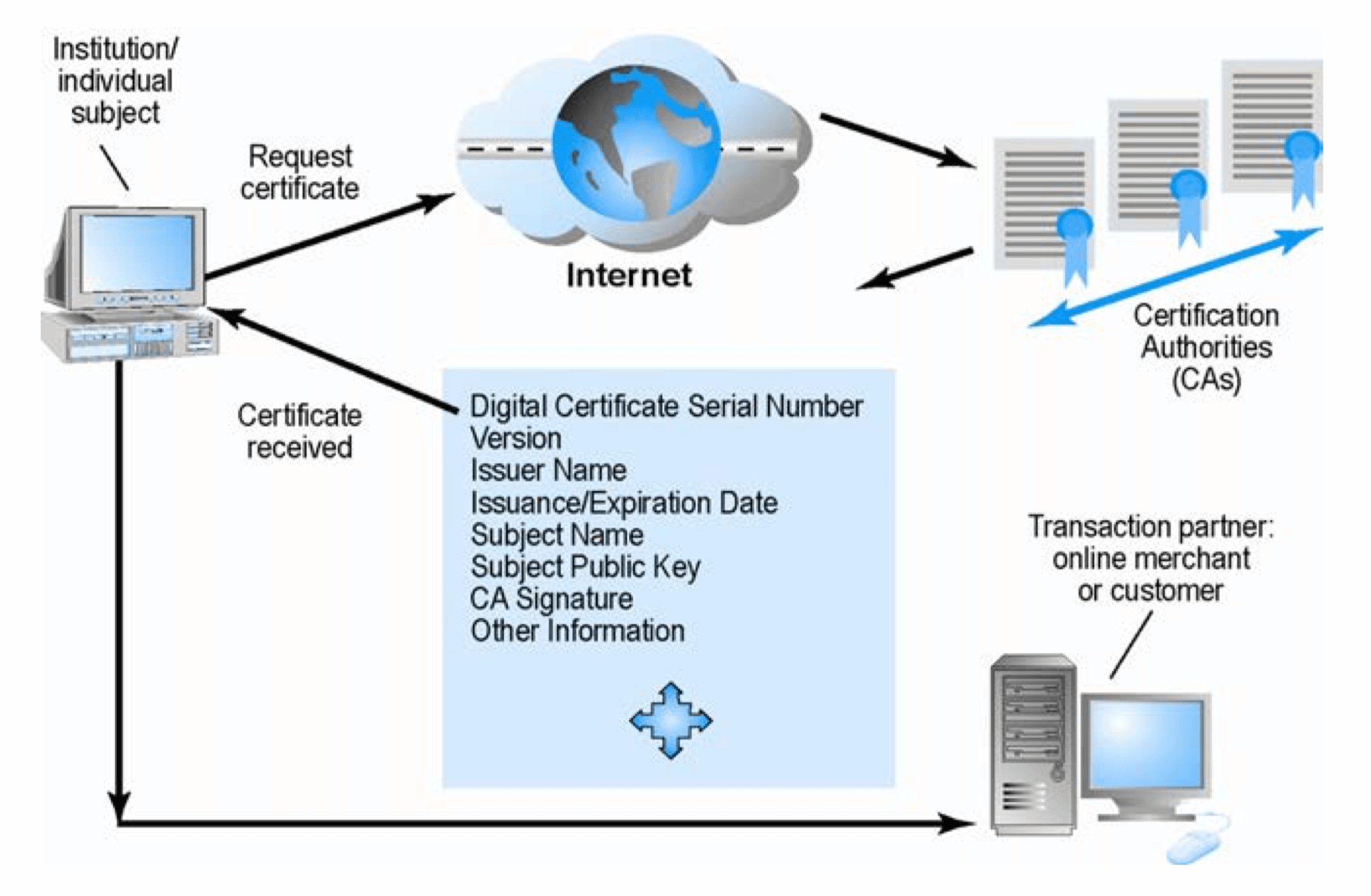
Digital Certificates and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Digital certificate
- Name of subjects/company
- Subject’s public key
- Digital certificate serial number
- Expiration date, issuance date
- Digital signature of certification authority (trusted third party institution) that issues certificate
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- CAs and digital certificate procedures that are accepted by all parties
Limits to Encryption Solutions
- Doesn’t protect storage of private key
- No guarantee that verifying computer of merchant is secure
- CAs are unregulated, self-selecting organizations